RedSDK unterstützt einen volumetrischen Umgebungstyp:
Abtragung ist ein optionaler Wert, um die Lichtstrahlverteilung zu stoppen, wenn der Ergebniswert unter dem Schwellenwert liegt.
- Lichtstrahl-Abtastschritt ist die Größe eines einzelnen Volumenschritts entlang des Lichtstrahls, der beim Abtasten des Mediums verwendet wird. Eine Verringerung dieses Werts erhöht die Renderqualität und -dauer, speziell für heterogene Medien.
- Streuende Proben definiert die Anzahl der Abtastungen, die während des mit den umgebenden Lichtern durchgeführten Beleuchtungsvorgangs beim Abtasten des Volumens verwendet werden. Eine Erhöhung dieses Werts erhöht die Renderqualitätt und -dauer für Volumen.
Struktur des Volumenform-Schattierers
Die Volumenform-Schattierer lässt sich über die Pfeilsymbole innerhalb der Baumstruktur auf der linken Seite des Render-Managers erweitern. Der Schattierer enthält folgende Einträge: Effekte, Volumetrischer Effekt, Sigma-Koeffizienten, Farbkanäle, Grenzverlauf (Kugel, Würfel oder Kein).
Ein angepasstes heterogenes Medium in einem Spotlicht-Volumen
Effekte
Die Szene ohne Medium
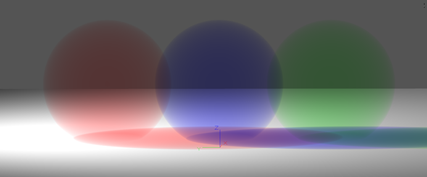
Homogener volumetrischer Standardeffekt
Volumetrischer Effekt
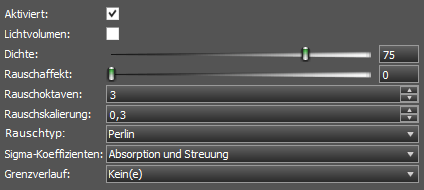
Schattiererparamter Volumetrischer Effekt
Aktiviert: Schaltet den volumetrischen Effekt ein/aus.
Lichtvolumen: Nur Lichtvolumen.
Dichte: Dichte des Mediums (0 – 100%).
Rauschaffekt: Rauschfaktor (0 – 100%).
Rauschoktaven: Eine Erhöhung der Anzahl der Oktaven erhöht den Rauschdetaillevel.
Rauschskalierung: Rausch-Zoomwert.
Rauschtyp: Rauschalgorithmus (Perlin oder Worley).
Sigma-Koeffizienten: Schattierer Sigma-Koeffizienten.
Grenzverlauf: Form des Grenzverlaufs (Kein, Kugel, Würfel).
Sigma-Koeffizienten
Schattiererparameter Sigma-Koeffizienten
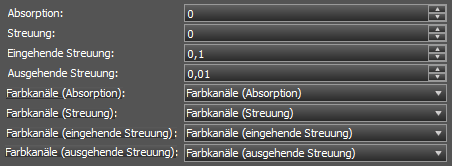
Absorption: Absorptions-Koeffizient.
Streuung: Streuungs-Koeffizient.
Eingehende Streuung: Streuungs-Koeffizient (wird nur verwendet, wenn Streuung = 0 ist).
Ausgehende Streuung: Streuungs-Koeffizient (wird nur verwendet, wenn Streuung = 0 ist).
Fabkanäle (Absorption): Schattierer Farbkanäle (Absorption). Wird nur verwendet, wenn Absorption = 0 ist.
Fabkanäle (Streuung): Schattierer Farbkanäle (Streuung). Wird nur verwendet, wenn Streuung = 0 ist.
Fabkanäle (eingehende Streuung): Schattierer Farbkanäle (eingehende Streuung). Wird nur verwendet, wenn Streuung = 0 ist.
Fabkanäle (ausgehende Streuung): Schattierer Farbkanäle (ausgehende Streuung). Wird nur verwendet, wenn Streuung = 0 ist.
Farbkanäle
Schattiererparameter Farbkanäle
Affekt: Farbaffekt (0 – 100%).
Rot: Roter Kanal.
Grün: Grüner Kanal.
Blau: Blauer Kanal.
Boundary shape (Sphere, Cube)
Boundary shape (Sphere) parameters
Centre - centre radius
Radius - sphere radius
Boundary density law – the law of the density changing near the surface of the boundary shape
Boundary density distance – distance to the surface of the boundary shape (0 – 100%)
Boundary density affect - affect of density’s change (0 – 100%)
Near - boundary layer only - switch on/off taking into account only the layer near the surface of the boundary shape
Near - boundary layer width – width of the layer near the surface of the boundary shape (0 – 100%)
Boundary shape (Cube) parameters
Min – first point of the box
Max - Second point of the box
Boundary density law – the law of the density changing near the surface of the boundary shape
Boundary density distance – distance to the surface of the boundary shape (0 – 100%)
Boundary density affect - affect of density’s change (0 – 100%)
Near - boundary layer only - switch on/off taking into account only the layer near the surface of the boundary shape
Near - boundary layer width – width of the layer near the surface of the boundary shape (0 – 100%)
Scattering medium.
Evironment may be Homogeneous or non-homogeneous medium with shadow.
Examples of Environmental turbulence with using the Prelin, Worley noise algorithms
It is possible to set up the environment inside the boundary shape (sphere , cube).
It is possible to use only the layer near the surface of the boundary shape.
It it is possible to Decrease/increase the environment density moving to the surface of the boundary shape.
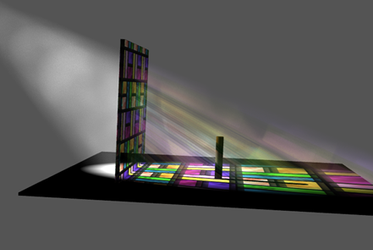
Examples of combining multiple volumetric effects (each effect has their own settings and boundary shapes).
Light scattering.
Support spot, point, beam light sources
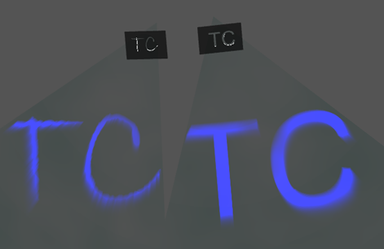
It is possible to create atmospheric effects (luminescence of celestial bodies, halo effects etc. )
It is possible Change the color of the rays when passing through the colored glass
It is possible to take into account only the highlighted space
Example of enabling or disabling the volume rendering during the global illumination
It is possible to create renders in holograms-like style
Known problems
- Error message when all volumetric effects are switched off.
- Disappearance of background image when volumetric effect is switched on.